Tau protein tangles, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, develop differently in women than in men, and spread faster and more easily in women. This comes from new research presented at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference this week, and suggests that treatments for Alzheimer’s may need to differ by gender.
How Do Tau Proteins Impact the Brain?
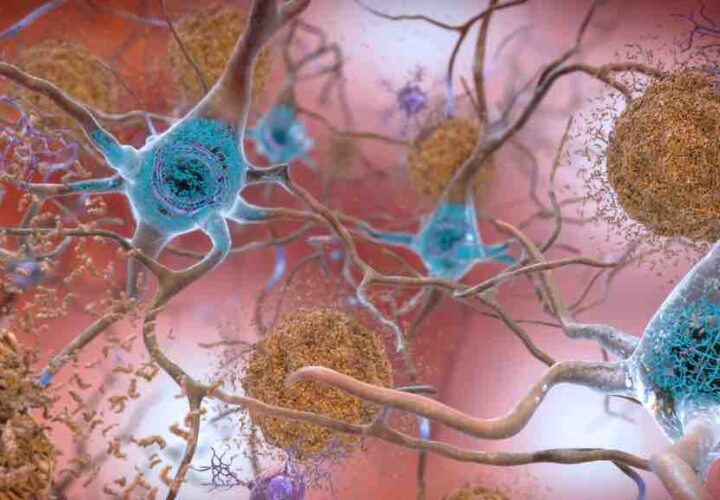
In healthy brains, tau protein binds to and stabilizes structures in brain cells called microtubules. In Alzheimer’s disease, tau proteins come apart from these microtubules and cling to each other instead. This results in tau tangles that kill off neurons.
It’s theorized that tau tangles may be the cause of Alzheimer’s disease symptoms. As tau tangles accumulate, the disease progresses and symptoms worsen. As more and more clinical trials targeting beta-amyloid plaques – another abnormal protein in Alzheimer’s patients – fail, scientists have turned their attention to tau.
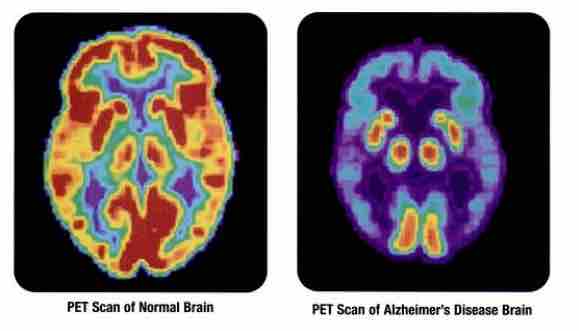
Evidence suggests that tau spreads through brain tissue like an infection, moving from neuron to neuron, turning normal tau proteins into toxic ones, and subsequently killing off brain cells. However, this study found that the way in which tau spreads appears to differ between men and women.
Why Tau Spreads Faster in Women Than Men
For the study, researchers from the Center for Cognitive Medicine (CCI) at Vanderbilt University Medical Center looked at the PET scans of healthy people and patients with mild cognitive impairment (a precursor to Alzheimer’s) to understand how tau spreads in the brain. They discovered that the structure of tau networks is different in men and women, with women having more “bridging regions” that connect various regions of the brain. This difference may be what allows tau to spread more easily across the brain, accelerating the development of Alzheimer’s disease in women.
According to the authors, this difference in tau architecture suggests a need for gender-specific Alzheimer’s prevention strategies, including earlier treatment, lifestyle interventions and cognitive remediation therapy (CRT) – i.e. brain training programs to improve cognitive function — in women.
Unrelated research presented yesterday at the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference suggests that following four healthy lifestyle habits can decrease the risk of Alzheimer’s by one-third in people who are at high genetic risk of the disease.
“Understanding how different biological processes influence our memory is a really important topic,” says Sepi Shokouhi, PhD, assistant professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences and lead investigator for the study. Sex-specific differences in the brain, she says, can help explain differences in neurodegenerative disorders and help the scientific community develop better treatments for conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, in both men and women.


Been tested for Dementia or Alzhemers with neuro/psych but he stated he spoke with my 3 grown daughters. (I have 2) and he said I failed testing so I am incapa le of raising my 2 adopted daughters age 15 & 17. And not to drive for fear I would get into wreck.However up until this I would drive 4 hrs from Tenn to IN nearly every weekend & back to my home in TN at end of weekend with. No problems or accidents. And this routine was this way for nearly 10 yrs.